LIAE架构人脸交换使用Pytorch实现
尝试使用Pytorch模仿DeepFaceLab的LIAE架构,做一个简单的人脸面部交换实验。原本的DeepFaceLab是使用TensorFlow实现的,并且包含了大量的开箱即用的工具,包括从数据预处理、模型训练、模型测试、模型推理、人脸预处理工具箱、交互式更换人脸GUI等等一套完整的在线和离线人脸素材交换工具所组成。所以项目本身非常庞大,所以此次任务只抽离出神经网络的部分,使用Pytorch实现,仅使用到DeepFaceLab的数据生成器。
LIAE架构
LIAE架构是DeepFaceLab项目中所使用的一种人脸交换架构,它通过学习人脸的特征和表情,将一个人的面部特征转移到另一个人的面部特征上。
LIAE框架的核心思想是将输入图像编码到潜在空间,然后在潜在空间进行调整,最后解码回图像空间。与传统的编码器-解码器框架不同,LIAE引入了更复杂的潜在空间处理机制。
与其他Encoder-Decoder架构相比,LIAE的编解码器结构本质上跟其他项目是差不多的,只是在整体结构上的潜在空间处理机制不同。
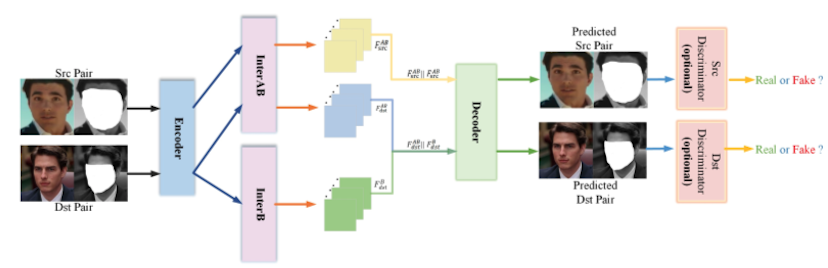
LIAE架构中通常设计中包含了2个Inter潜在信息模块,分别是InterB和InterAB,它们的与编解码器组合的Pipeline计算如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
src_code = encoder(src)
src_inter_AB_code = inter_AB(src_code)
src_code = torch.cat((src_inter_AB_code, src_inter_AB_code), dim=1)
dst_code = encoder(dst)
dst_inter_B_code = inter_B(dst_code)
dst_inter_AB_code = inter_AB(dst_code)
dst_code = torch.cat((dst_inter_B_code, dst_inter_AB_code), dim=1)
pred_src, pred_src_mask = decoder(src_code)
pred_dst, pred_dst_mask = decoder(dst_code)
通过forward流程可以看出,对SRC图像的自编码重建仅使用InterAB的code,对于DST图像的生成则使用InterB和InterAB的code进行concat后进行解码得出。
对于Encoder的实现,需要考虑到UDT模式的设计:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, e_channels, opts=["u", "d", "t"]):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.in_ch = in_channels
self.e_ch = e_channels
self.opts = opts
if "t" in self.opts:
self.down1 = Downscale(self.in_ch, self.e_ch, kernel_size=5)
self.res1 = ResidualBlock(self.e_ch)
self.down2 = Downscale(self.e_ch, self.e_ch * 2, kernel_size=5)
self.down3 = Downscale(self.e_ch * 2, self.e_ch * 4, kernel_size=5)
self.down4 = Downscale(self.e_ch * 4, self.e_ch * 8, kernel_size=5)
self.down5 = Downscale(self.e_ch * 8, self.e_ch * 8, kernel_size=5)
self.res5 = ResidualBlock(self.e_ch * 8)
self.downscale_factor = 32
else:
self.down1 = DownscaleBlock(
self.in_ch,
self.e_ch,
n_downscales=4,
kernel_size=5,
)
self.downscale_factor = 16
self.out_ch = self.e_ch * 8
def forward(self, x):
if "t" in self.opts:
x = self.down1(x)
x = self.res1(x)
x = self.down2(x)
x = self.down3(x)
x = self.down4(x)
x = self.down5(x)
x = self.res5(x)
else:
x = self.down1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
if "u" in self.opts:
x = x * torch.rsqrt(torch.mean(x**2, dim=1, keepdim=True) + 1e-06)
return x
def get_downscaled_resolution(self, res):
return res // self.downscale_factor
def get_output_channels(self):
return self.out_ch
Inter模块的设计用于将编码器输出的特征图转换为潜在空间,并进行上采样或下采样。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
class Inter(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ae_channels, ae_out_channels, resolution, opts=["u", "d", "t"]):
super(Inter, self).__init__()
self.opts = opts
self.in_ch = in_channels
self.ae_ch = ae_channels
self.ae_out_ch = ae_out_channels
self.dense_res_factor = 32 if "d" in self.opts else 16
self.lowest_dense_res = resolution // self.dense_res_factor
self.need_upscale = "t" not in self.opts
self.dense_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_channels, ae_channels),
nn.Linear(ae_channels, self.lowest_dense_res * self.lowest_dense_res * ae_out_channels)
)
if self.need_upscale:
self.upscale = Upscale(ae_out_channels, ae_out_channels)
self.out_res = self.lowest_dense_res * 2 if self.need_upscale else self.lowest_dense_res
def forward(self, inp):
x = self.dense_layers(inp)
x = x.view(-1, self.ae_out_ch, self.lowest_dense_res, self.lowest_dense_res)
if self.need_upscale:
x = self.upscale(x)
return x
def get_downscaled_resolution(self):
return (
self.lowest_dense_res * 2 if "t" not in self.opts else self.lowest_dense_res
)
def get_output_channels(self):
return self.ae_out_ch
Decoder的实现需要使用双分支的方式同时输出RGB图像和Mask图像。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, d_channels, d_mask_channels, opts=["u", "d", "t"]):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.opts = opts
self.use_dense = "d" in opts
self.is_transformer = "t" in opts
self.in_ch = in_channels
self.d_ch = d_channels
self.d_mask_ch = d_mask_channels
self.main_path = nn.ModuleList()
self.mask_path = nn.ModuleList()
if self.is_transformer:
num_blocks = 4
channels = [in_channels, d_channels * 8, d_channels * 8, d_channels * 4, d_channels * 2]
mask_channels = [in_channels, d_mask_channels * 8, d_mask_channels * 8, d_mask_channels * 4, d_mask_channels * 2]
else:
num_blocks = 3
channels = [in_channels, d_channels * 8, d_channels * 4, d_channels * 2]
mask_channels = [in_channels, d_mask_channels * 8, d_mask_channels * 4, d_mask_channels * 2]
for i in range(num_blocks):
self.main_path.append(
DecoderBlock(channels[i], channels[i+1], kernel_size=3)
)
for i in range(num_blocks):
self.mask_path.append(SimpleUpscale(mask_channels[i], mask_channels[i+1], kernel_size=3))
if self.use_dense:
if self.is_transformer:
self.mask_path.append(SimpleUpscale(mask_channels[-1], d_mask_channels * 1, kernel_size=3))
self.mask_path.append(SimpleUpscale(mask_channels[-1], d_mask_channels * 1, kernel_size=3))
else:
self.mask_path.append(SimpleUpscale(mask_channels[-1], d_mask_channels * 1, kernel_size=3))
if self.use_dense:
if self.is_transformer:
self.rgb_output_dense = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
])
else:
self.rgb_output_dense = nn.ModuleList([
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=0),
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=0),
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=0),
nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=3, padding=0)
])
self.mask_output = nn.Conv2d(d_mask_channels * 1, 1, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
else:
self.rgb_output = nn.Conv2d(channels[-1], 3, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
self.mask_output = nn.Conv2d(mask_channels[-1], 1, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, z):
x = z
for i, block in enumerate(self.main_path):
x = block(x)
if self.use_dense:
rgb_outputs = []
for conv in self.rgb_output_dense:
rgb_outputs.append(conv(x))
yy = torch.cat(rgb_outputs, dim=1)
x = torch.sigmoid(F.pixel_shuffle(yy, 2))
else:
yy = self.rgb_output(x)
x = torch.sigmoid(yy)
m = z
if self.is_transformer:
for i in range(4):
if i < len(self.mask_path):
m = self.mask_path[i](m)
if self.use_dense and len(self.mask_path) > 4:
m = self.mask_path[4](m)
else:
for i in range(3):
if i < len(self.mask_path):
m = self.mask_path[i](m)
if self.use_dense and len(self.mask_path) > 3:
m = self.mask_path[3](m)
yy_mask = self.mask_output(m)
m = torch.sigmoid(yy_mask)
return x, m
从本质上来看,这个结构与其他FaceSwap类型的项目相比,最大的区别在于它使用了2个Inter潜在信息模块,这两个潜在信息模块应该是这个任务中的关键所在。
损失函数
从官方相关的资料来看,损失函数最主要的是DSSIMLoss。DSSIM主要用于衡量两张图像之间的相似性,它考虑了图像的亮度、对比度和结构等特征。
从网络上其他出处来看,DSSIM考虑的场景是当一个图像进行了一些特殊的变换如亮度、对比度或模糊等处理后,使用L1或L2来计算损失可能会得到与预期不相符的结果,所以引入了结构相似性指数(Structural Similarity Index measure,SSIM),通过计算两张图像的相似性来更准确衡量它们之间的差异。从图像生成式的一些任务来看,这确实是更符合图像从最初低分辨率到高分辨率生成过程中所需精准的监督信号。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
class DSSIMLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, filter_size=11, device=None, max_val=1, k1=0.01, k2=0.03):
super(DSSIMLoss, self).__init__()
self.max_val = max_val
self.filter_size = filter_size
self.device = device
self.filter_sigma = 1.5
self.k1 = k1
self.k2 = k2
self.c1 = (self.k1 * self.max_val) ** 2
self.c2 = (self.k2 * self.max_val) ** 2
self._create_gaussian_window()
def _create_gaussian_window(self):
gaussian_1d = cv2.getGaussianKernel(self.filter_size, self.filter_sigma)
gaussian_1d = torch.tensor(gaussian_1d, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device)
gaussian_2d = gaussian_1d @ gaussian_1d.t()
self.window = gaussian_2d.expand(3, 1, self.filter_size, self.filter_size).contiguous()
def _compute_local_stats(self, x, y):
mu_x = F.conv2d(x, self.window, padding="valid", groups=3)
mu_y = F.conv2d(y, self.window, padding="valid", groups=3)
mu_x_sq = mu_x.pow(2)
mu_y_sq = mu_y.pow(2)
mu_xy = mu_x * mu_y
var_x = F.conv2d(x * x, self.window, padding="valid", groups=3) - mu_x_sq + 1e-6
var_y = F.conv2d(y * y, self.window, padding="valid", groups=3) - mu_y_sq + 1e-6
cov_xy = F.conv2d(x * y, self.window, padding="valid", groups=3) - mu_xy + 1e-6
return mu_x, mu_y, mu_x_sq, mu_y_sq, var_x, var_y, cov_xy
def forward(self, img1, img2):
mu1, mu2, mu1_sq, mu2_sq, sigma1_sq, sigma2_sq, sigma12 = self._compute_local_stats(img1, img2)
luminance_term = (2.0 * mu1 * mu2 + self.c1) / (mu1_sq + mu2_sq + self.c1)
contrast_term = (2.0 * sigma12 + self.c2) / (sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + self.c2)
ssim_map = luminance_term * contrast_term
ssim_map = torch.clamp(ssim_map, min=0.0)
return (1.0 - ssim_map.mean()) / 2.0
训练结果
训练的技巧保持与DeepFaceLab官网实现的训练技巧和一些超参数基本一致,使用DSSIMLoss监督生成图像过程的相似度,使用L1Loss监督五官部分的像素信号如鼻子嘴巴等,同时需要使用L2Loss监督生成的人脸区域像素和人脸区域的Mask。并且需要把五官部分的loss进行大比例加权,确保五官部位的生成质量。
以LIAE-UDT的结构为例,训练256分辨率的图像,代次数在58000时,第一阶段基本可以停止,通过历史数据可以看到处于收敛状态。根据生成的sample和loss调整一下参数后,继续训练第二阶段。 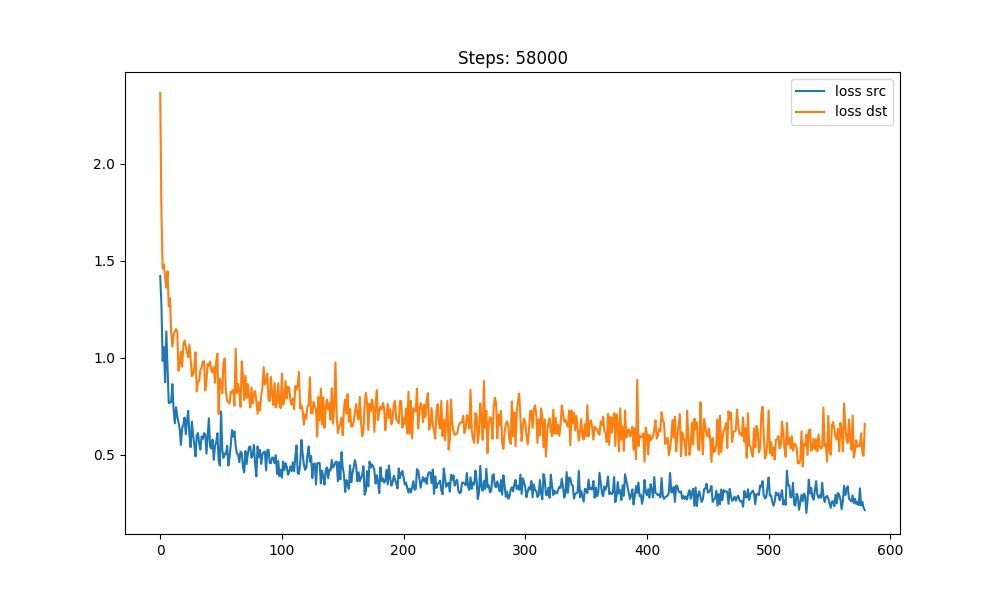
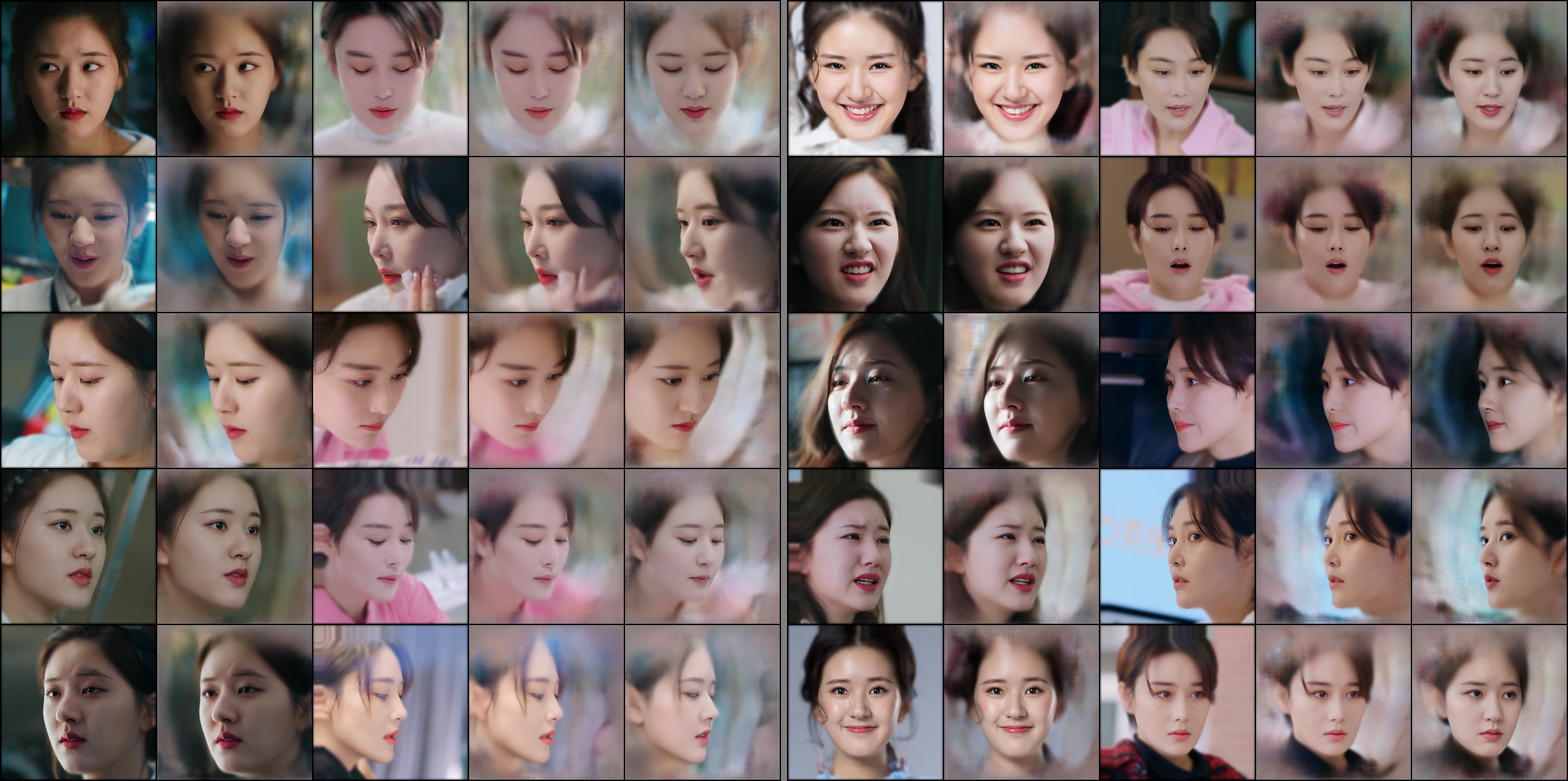
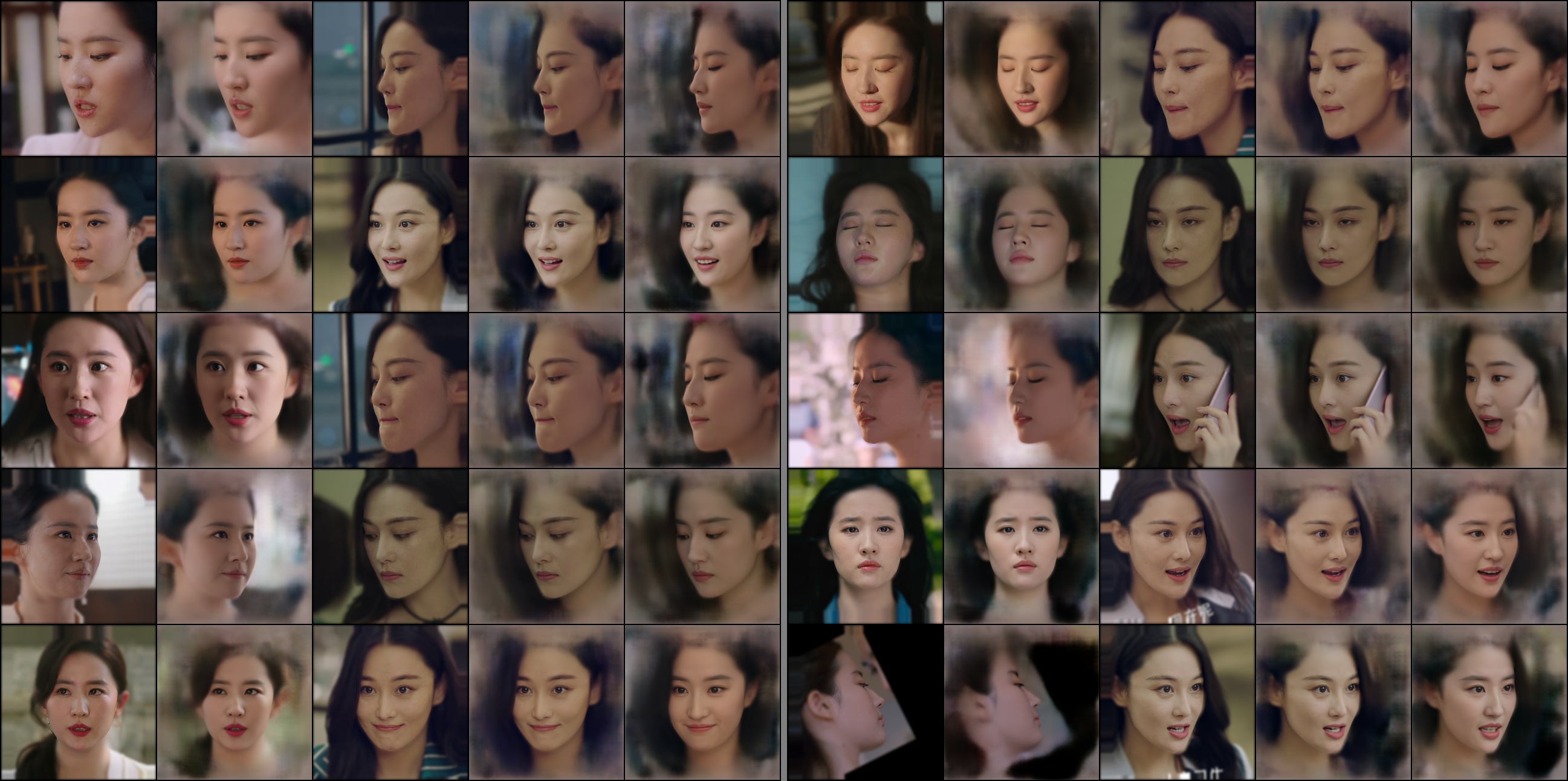
在经历了100000多次的迭代后loss基本稳定,训练效果如下:
从生成效果来看SRC的重建和DST的生成效果均与DeepFaceLab的生成效果基本一致,尤其是一些脸部肌肉和光影效果在迭代较多次数后也趋近于较好的效果,由于目前手上只有一张闲置的3060 12G显卡,所以实验只能尝试到256的分辨率,有空尝试一下512的效果可能会遇到其他需要解决的问题。